Data Structure
from GoValley Algorithm Camp
1. Introduction
2015年超过10W人成功申请到了H1B工作签证计算机工程类 科技公司工作时间弹性强,无强制要求 I: Software Development Engineer 11、12万USD 年薪 超过90%职业 十四周 28节课 大概8-10小时准备每周
Interview Process
面试成功后,公司还是会全方位进行培训
- Resume
- 简历优化
- 校招、海投、内推
- HR Phone Interview
- 15-30mins
- Self-Introduction: 优点、编程语言、Projects
- Fundamental Questions about CS: 有标准答案的问题(非常简单)
- Phone Screen Technical Interview
- 50min - 1hour
- online coding (2-3)
- 数据结构与算法问题
- On-site Interview (一般两轮)
- Coding Algorithms (Whiteboard)
- Design and Architecture
- Technical Communication (就简历展开提问)
- Host Manager (某个组的大概方向,主观性强)
- Offer
- Review and Negotiation
课程大纲 Syllabus
- Introduction
- Algorithms (20节课)
- Design (2-3)
- Basic Key Points (1-2)
- Exercise (3)
- Interview Skills
- mid-term and final (2) 直接挂钩内推
Algorithm
LeetCode 做作业为主 有针对性的做题 咨询老师
Others
- Java 授课
- Homework 周四早上交作业
- Shouldn’t memorize solutions, try to categorize and ‘Juyifansan’
- Whiteboard coding, don’t use IDE
2. Time Complexity 时间复杂度
符号: O, 表示程序需要运行的最小次数,给最简单上界
- 最坏情况(Worst Case):任意输入规模的最大运行时间。(如春节抢红包)
- 平均情况(Average Case):任意输入规模的期待运行时间。(一般情况下)
- 最佳情况(Best Case):通常最佳情况不会出现。(最好情况下)
f(n) = n² + 2n + 5 f(n) ⊂ O(n²)
f(n) = n + 7 f(n) ⊂ O(n)
复杂度 (-) | 标记符号(-) | 描述 (-)
Constant | O(1) | 操作的数量为常数,与输入的数据规模无关
Logarithmic | O(log2 n) | 操作的数量与输入数据n的比例为 log2 (n)
Linear | O(n) | 操作的数量与输入数据n成正比
Quadratic | O(n2) | 操作的数量与输入数据n的平方成正比
常用需要记住 Sort 的时间复杂度为 O(nlogn) Binary Search 的时间复杂度为 O(logn)
3. Array
A data structure consisting of a collection of elements, each identified by at least one array index or key
最基本的数据结构
##三大特性
- Continuous Space
- 连续存储,连续空间
- Linked List (链表) 就不属于连续空间
- Same Type Elements
- 根据语言类型有所不同 但一般要求相同类型元素
- 如字符串,就是一个字符的array
- Identified by Index
- addr(elem) = addr(head) + sizeof(elem)*index
- 每存取一个elem的需要固定时间 O(1) 数组是最基本的数据结构 其他各种数据结构,如队、栈、hash都是基于最基本的数组来构建的
//定义数组
int[] a = new int[5];
a.length // 返回5
//Java Library (pre-defined 数据结构)
ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>(5)
为什么需要数组
To make code Simple and Clean
完成很多重复性工作时 使用 数组+循环 比较简单
Basic Operations
当使用ArrayList结构时,下列数组方法可以使用
- Get <index> O(1)
- Set <index,value> O(1)
- Add <opt_index, value> O(n)
- 加入index的时候,后面的所有元素依次向后移
- Remove <index/value> O(n)
- Find <value> O(n)
//如何实现一个ArrayList,有可能会直接考
public class ArrayList{
private int capacity; //容量,申明多大的空间
private int size; // 实际有多少数据
private int[] data;
//初始化函数
public ArrayList(int capacity_){
capacity = capacity_;
size = 0;
data = new int[capacity];
}
//Get
public int get(int index) { //要返回int 所以函数类型是int
if (index < 0 || index >= size){
// throw exception
// 确保在请求不存在信息时什么也不做
}
return data[index];
}
//Set
public void set(int index, int value){ //只修改 不返回 所以是空类型函数
if (index<0 || index >=size){
//throw exception
}
data[index] = value;
}
//Add
public void add(int index, int value){
if (index < 0 || index > size){
// throw exception
}
if (size == capacity) {
resize();
}
size++;
for(int i = size; i > index; i--){
data[i] = data[i-1];
}
data[index] = value;
}
private void resize(){ //给array地址扩容
capacity *= 2; //扩容
int[] temp_data = new int [size];
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
temp_data[i] = data[i];
}
data = new int[capacity]; //重新把新申明的空间赋给data,但是得先用temp_data去把原数据保存一遍
for(int i = 0; i < size; I++){
data[i] = temp_data[i];
}
}
//remove
public void remove(int index) {
if (index<0 || index >=size){
// throw exception
}
size--;
for (int i = index; i < size; i++){
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
}
}
面试写ArrayList所需要注意的问题
- Key data storage, data[]
- Initialize the capacity
- Always Check Bound
- Resize
数组面试问题
Warmup Question
- sum of the array number
- minimum element of the array
- second minimum element of the array
- swap two element in an array Two Sum
input: number = {2, 7, 11, 45}, target = 9; output: {2,7} 在开始写代码前,先把解决方案用自然语言清楚的描述给面试官听,确保非计算机人员能够听懂,这样再去把想法变成code
//解决方案1: O(n^2)
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target){
int[] result = new int[2];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length, i++){
for(int n = i+1; n < nums.length; n++){
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target){
if(nums[i] > nums[j]){
result[0] = nums[j];
result[1] = nums[i];
} else {
result[0] = nums[i];
result[1] = nums[j];
}
}
}
}
}
//解决方案2:先把数组有小到大排序,将两头的数相加,如果大于target,那么舍掉打的数,如果小于target,那么舍掉小的数,直到找到解。 这个算法最常出现!!!
//O(nlogn) 排序复杂度+O(n) 寻找复杂度
##双指针 instead of using one pointer, using two pointers to traverse the array in the same/opposite direction
- Sorted O(nlogn)
- Find two or two set of numbers subjected by certain condition 重点题型(在eclipse 均进行过练习)
two-sum (duplicated), three-sum, k-sumReverse ArrayOdd Even SortPivot SortRemove ElementMerge Two Sorted ArrayPartation Array
## 4. Binary Search
给出一个数组和一个目标数,返回该目标数所在数组内的下标 Binary Search 的时间复杂度一般是 O(logn), 小于遍历 O(n)
- 定义begin 和end 千万注意临界的选择 begin=0; end=length or length-1
- p = (begin+end)/2
- 比较P和目标数,返回下标 重点在于区分 左闭右开区间[) 和 闭区间[]
//左闭右开区间[) begin = 0, end = num.length
if(num[p] < target){
begin = p + 1;
} else {
end = p; //右开,和最初定义 end = num.length 一个道理
}
//对于左右闭合区间[] begin = 0, end = num.length - 1
if(num[p] < target){
begin = p + 1;
} else {
end = p - 1; //右闭,和最初定义 end = num.length-1 一个道理
}
// 记住记住记住!!! 不要琢磨奇偶数的区别 记住区间性就不会写错了...
重点题型
Binary Search
Sqrt(X): 从1, 2, 3, 4… X之间找到X的平方根
Search In Rotated Sorted Array
Search the minimum number in Rotated Sorted Array
Find a number in a 2D matrix
5. Linked List 链表
##Java Variables & Data Types
- Primitive Type 基础数据类型
- byte, short
- Stack Memory
- 直接储存值
- e.g: int a = 5
- 直接把5(右边) 赋给 a(左边)
- Reference Type 引用数据类型
- 以New开头 String str = new String(“sbc”)
- 以数组类型存在的 int[]
- Heap Memory
- 申明一片空间 (address)
- MyObject obj = new MyObject();
- 栈中存储的地址会指向堆中的一片空间,所以叫做引用型,如下图
- 把obj的地址指向堆里面的一片地址, 所以如果obj1 和obj2 同时指向了一片空间*(MyObject obj2 = obj1)*,那么对任何obj的修改都会影响obj1 和obj2.  
在Java中,在函数传参时,不论基本数据或引用数据,都是复制了一个新的数据,有时不会影响原来的数据,和JavaScript不同。
基本数据类型不会影响原来的数据,只会影响复制的新值
public void increase(int a){
a = a + 1;
System.out.print(a);
}
public static void main(){
int a = 5;
increase(a); // print 6.
System.out.print(a); // print 5.
}
引用数据类型会影响原来的数据内容,因为复制的是一个地址,指向的还是原来的那一片空间中的内容 
Linked-List
链表思想比较直白,但是考核一个人细节上的严谨程度,如空指针,边界等数组可以随时找到任何一个元素的下标  每一个节点都链接着下一个节点,所以如果知道第一个节点,就一定可以知道后面的 很多时候我们不知道需要储存数据的大小,需要多少内存。 数组需要自己分配一片内存,而链表里每个节点是离散的,可以随时扩充 基本操作 ListNode 表示链表节点
public class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val_){ //构造函数 有自己的值 也包含下一个ListNode
val = val_;
next = null;
}
}
LinkList 表示链表
public class LinkedList{
private ListNode head = null;
private ListNode tail = null;
private int size = 0;
public get(int index){}; //见Eclipse实现
public void set(int index, int value){};
public void add(int index, int value){};
public void remove(int index){}; // java垃圾回收机制会回收没有被指向的节点
//不用写构造函数的时候会默认生成一个空的构造函数,不要紧
在考虑add和remove时,一定要考虑head的特殊性,因为它没有前置节点利用一个虚拟的dummy节点让head也拥有前置节点,这样head也有前驱,不需要特别的为特殊情况进行考虑 做add 或 remove 题目时一定要使用dummy节点 
//带dummy的add操作
public void add(int index, int value){
checkBoundsExclusive(index);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1)
}
链表题型
- Count Related 只给一个NodeList,不需要LinkedList类,不需要改变整个连表结构,不需要dummy Linked List Length 解其他链表题,可以把这个封装起来让逻辑更清晰 Kth Node from the end 1. 遍历 2. 双指针同速不同时开始 Middle Node 1. 遍历 2. 双指针不同速同时开始 与面试官沟通好middle node 具体指什么 商量好就行 Linked List Cycle 判断是否有环(无限链表 指向之前的某一个node) 高级版 链表环 找出开始循环的那个node 注意k其实等于l2 
- Structure Related
需要修改结构的话 时刻考虑需会不会修改head 需不需要dummy节点
Remove Duplicate from Sorted ListMerge sorted ListReverse Linked List a->b->c->d to d->c->b->a
#6. Stack & Queue 重点注意Array 和 Stack, Queue, LInkedList 等数据结构的相互转换,这样考察对这些基本数据结构的理解。
Stack (FILO)
在实际软件开发的过程中,能不用递归就不用递归,用迭代(for & while)Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
包含Pop, Push, Size, Peek操作
在操作系统中,栈Stack 比 堆Heap 快
Queue (FIFO)
- size
- remove (poll)
- add (offer)
- element (peek)
题型
- Implement Queue using Stacks Calculate time complecity
- a stack with max() / min() time <-> space
- Valid Parentheses 括号
- Bad Hair Day 单调栈的用法
- Largest Rectangle in Histogram 最好自己做一次
7. Recursion 递归
解决问题的方法里,有一些子问题可以用原来的方法解决,一层一层解决下去,直到有一层能够得到明确答案。用同样的方式解决量级不同的问题 是一种将大问题分解为小问题的思路,小问题被解决了,才能解决大问题。 经典题型: Factorial(阶乘) Fibonacci Number(斐波那契数列) Termination(Base) Case 中止条件 最简单 没有子问题的问题 Recursion 递推关系 是一系列分解问题 逐层减小问题规模的Rules
- 定义问题相关的参数(阶乘的个数 汉诺塔的个数 简单)
- 定义临时储存结果或状态的参数 (辅助性参数 是f(n)和f(n-1)中间的隔着的那一层 较难想到 想讲出自然语言 转换为伪代码 最后转换为代码)
- 定义一个void函数去处理刚才定义的那些参数 F(n)<=g(F(n-1))
function Factorial(int n){
if(n==1){ return 1; } //中止条件
return n*Factorial(n-1); //递推关系
}
function Fibonacci(int n){ //1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55...
if(n == 1){ return 1; }
if(n == 2){ return 2; }
return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);
}
题型 Fn==> F(n-1)
Tower of Hanoi
回溯递归 Backtracking
F(n)有多个结果 每个结果递归后又有更多的结果… 这种情况下 递归更像是一种全局试错的过程 如0-1背包问题, maze迷宫问题, eight queen八皇后问题(最重要) 关键在于想清楚逻辑,务必写出伪代码,再直接转为代码逻辑处理在伪代码阶段,实际编码时可以少考虑逻辑,专注编码即可 对回溯问题, 首先,定义好base case, 其次,return case1 || case 2 || case 3
#8. Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Progamming VS Recursion DP能解决的问题一般都能用Recursion解,但是不是所有的Recursion题目都能用DP来解。 但是DP一般要比Recursion快,占用更多空间,因为它用时间换了空间
什么时候选择DP?
recursion 题目,但不是 tail recursion 伪递归的时候
(伪递归,在函数最后重新调用自己,随时可以转化为for循环)
需要有最优子结构
recursion 出现了大量多余计算的时候
用更多的空间去减少计算量 (设定最优解答的表,然后去填表)
原理/如何使用
思考recursion解法,确认DP合适求解
找到最优子结构,用记忆的方法减少redundancy
用一个额外的空间,把所有temporary result记录下来
例子 - 斐波那契数列(一维)
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, …
//递归解法 public int solution1(int n){ if(n==0 || n==1) return 1; return solution1(n-1) + solution1(n-2); //最优子结构 }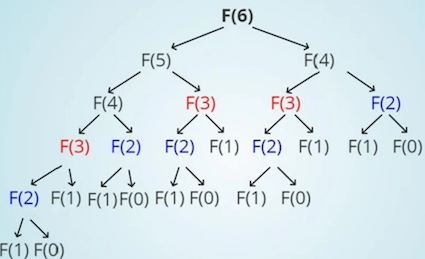
能够很明显的看到,F(6), F(5)在递归过程中被计算了一次,F(4)被计算了两次,F(3)被计算了3次,F(2,1,0)被重复计算了n次… 所以使用动态规划
//动归解法 public static int fabonacci(int n){ if(n<1) return 1; //边界条件 //重要:创建一个数组空间,存放所有的临时变量,后面只需要填写这个数组,不需要重复计算 int[] result = new int[n+1]; result[0] = 1; //初始值 result[1] = 1; //初始值 //重要:使用for 循环开始填补数组,简单的是一维循环,维度越高越难 for(int i = 2; i<n+1; i++){ result[i] = result[i-1] + result[i-2]; } //数组填满以后,结果自然出来 return result[n]; }例子 - Unique Path (二维)
在长宽分别为m,n的格子里,只能向下或者向右走,从左上到右下,求有多少种不同的走法
// recursion public static int solution1(int m, int n){ if(m == 1 || n == 1) return 1; return solution1(m-1, n) + solution1(m, n-1); //最优子结构 }可以想象,有些格子,被重复计算了,如下图的红点,在他的左边和下边格子计算时,都把他重新计算了一次,出现了冗余计算的情况,所以可以使用动态规划
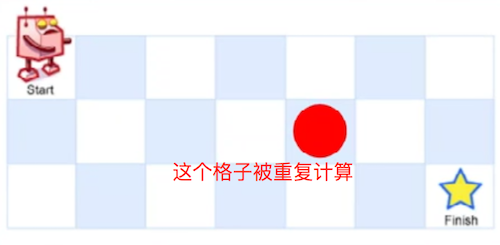
public static int solution2(int m, int n){ int[][] result = new int[m][n]; //填一个二维数组 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ //横着的第一行全部都是1 result[i][0] = 1; } for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ //竖着的第一列也都是1 result[0][i] = 1; } for(int i = 1; i < m; i++){ //其他格子可以用上面左边的格子和去计算 for(int j = 1; j < n; j++){ result[i][j] = result[i][j-1] + result[i-1][j]; } } return result[m-1][n-1]; //格子填完,答案也就出来了 }
题型
- 0-1 背包
- Longest Increase Subsequences
- Longest Common sequences
- Edit Distance
- Matrix Multiplication
- [重要] Maximum Subarray
9. Tree
A tree is a data structure made up of nodes or vertices and edges without having any cycle.
有环的情况叫做 “图”
链表(没有环的情况下)也是一种树,有节点,有指针
文档系统就是最典型的树状结构
概念
- Nodes
- Root: 有且只有一个root, 没有指针指向Root
- Left: 没有任何指针指向别人的节点
- Parent: 父节点
- Children: 子节点
- Sibling: 兄弟节点
- Ancestor: 祖先节点
- Descendant: 后代节点
- Edge: 指针
- Num(node) = Num(Edge) + 1 因为每一个node都有一个edge,但是root没有edge
- Height: 高度,指从 root 到最底层 leaf 有多少层节点
- Depth: 深度,指从 root 到最底层 leaf 有多少层边 edge
- 与节点和指针的关系一样 Height = edge + 1
- Level: 层,root 是 Level0,依次类推
- 每一层level上的点到Root的距离是一样的
- 第n层节点需要从 root 走n步
- Path: 路径,如何从一个节点走到另一个节点
Binary Tree
A tree that each node can has at most two children, called left child and right child
complete binary tree
常常被用来模拟计算二叉树的时间复杂度,以及堆 heap 也是一种complete binary tree
the sum of the paths are the smallest
二叉树性质
Level i 最多有 2^i 个node
height 为 k 时,最多有 2^k - 1 个节点 (0+) 2+4+8+…+ (2k-1) = (0+2k-1)*k/2 = 2^k -1
反之,当一个complete binary tree 有n个节点时,height 的值为 [log2(n+1)]
对一个 complete binary tree 来说,如果某个节点的数是k,那么他的 left child 是 2k+1,right child 是 2k+2
如何存储? 对一个节点为 n 的 complete binary tree 来说,直接开一个大小为n的数组
array 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CB tree index r f r ff fr rf rr fff ffr 根据index来找具体的值
CB tree value A B C D E F G H I
如: array[k] 的父亲一定是 array[(k-1)/2] 5(rf) 的父亲是 2® 8(ffr)的父亲是 3(ff)
构造一个 complete binary tree
Public class BinaryTree<T>{ private Nod e<T> root; public Tree(T rootData){ root = new Node<T>(); root.data = rootData; } public static class Node<T>{ private T data; private Node<T> leftNode; private Node<T > rightNode; } }
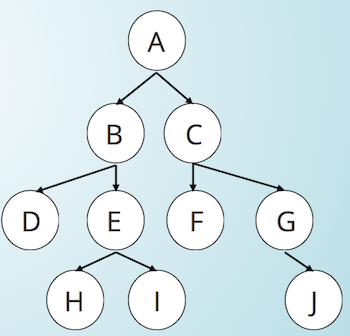
专题一: 遍历 Traversal
Pre-Order: parent —> left child —> right child
A - B - D - E - H - I - C - F - G - J
In-Order: left child —> parent —> right child
D - B - H - E - I - A - F - C - G - J
Post-Order: left child —> right child —> parent
D - H - I - E - B - F - J - G - C - A
可以使用 recursion 遍历,不推荐
可以使用 Stack 遍历,很重要
专题二: 构造 Binary Tree
通过遍历来的结果,重新构造二叉树,但结果不唯一
- 只给一种,结果不唯一
- 只给两种
- 有 in-Order,结果唯一,因为前后序可以确定root,in-order 可以确定左右两边,然后递归
- 无 in-Order,结果不唯一
- 三种全给,结果唯一
Binary Search Tree (BST) 二叉搜索树
适用情况:in-order 遍历结果是个 严格的上升序列
换句话讲,所有的left-child 都小于响应的 right-child
- find: 比较 target 与 node 大小,大了去left找,小了去right找
- add:
- delete:
Depth First Search 深度优先搜索
one root, and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
一根线出去, 单方向一路走到头,最坏情况下会遍历所有可能性
换句话说,就是递归在二叉树上的应用
应用
- Recursion and backtrace
- stack
- solve some tree problems
注意:做题时切记考虑到所有左孩子,右孩子的edge case
Breadth First Search 广度优先搜索
one root, and explores by neighbour node, 遍历层级,level1 遍历后遍历 level2
一层一层展开,直到走到最末端
通过队列来实现:
Queue<element> queue = new LinkedList<element>()
//add
boolean offer(element e);
//remove: 弹出元素
element poll();
//element: 查看元素,不弹出
element peak();
方式一: double Q
Q1 加入 root,开始弹root,并且新建Q2,加入 root 的左右孩子,then Q1 = Q2 …. 当Q1 为空,退出
Queue<TreeNode> q1 = new LinkedList<>(); q1.offer(root); while(!q1.isEmpty()){ Queue<TreeNode> q2 = new LinkedList<>(); while(!q1.isEmpty()){ TreeNode top = q1.poll(); //visit top if(top.left != null) q2.offer(top.left); if(top.right != null) q2.offer(top.left); } q1 = q2; }
方式二:single Q
不分层级的概念,弹出一个节点的时候,把它的字节点全部加入到queue 里,实现全部遍历 并不知道哪个是哪一层,但是一样实现遍历功能
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode top = queue.poll(); //visit top if(top.left!=null){ queue.offer(top.left); } if(top.right!=null){ queue.offer(top.right); } }
应用
- find minimum path / distance / …
- Queue
- word ladder I/II
10. Heap
计算机系统进程: Heap (min, max)
是一种 tree-based data structure, 于是分出了min-heap 和max-heap
Min-Heap: root is always smaller than children
Max-Heap: root is always larger than children
最常见的实现是根据 完全二叉树 Complete Binary Tree 来实现的,如下图
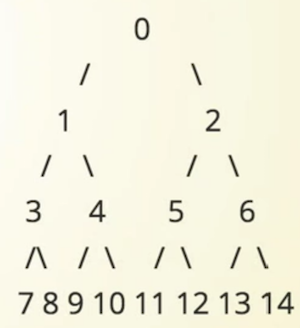
完全二叉树
是指除最后一行以外,其余行都是满的,二叉树 对于完全二叉树,可以不用left 和right,而用下标来表示,如下图所示

- index of children = 2n + 1 , 2n + 2
- index of parent = n - 1 / 2
基本操作
- insert O(log n)
- delete O(log n)
- initilize O(n)
- Insert element one by one: O(n * log n)
- dump all element at once, then sift down level by level: O(n)
Java 中的应用: PriorityQueue
Operations:
E peek();
E poll();
boolean offer(E element)
Constructor:
PriorityQueue(int capacity)
How does Java know how to compare elements in the heap
- Compartor: 比较器,帮助其他东西进行比较
class MyCompartor implements Comparator<MyClass>{ public int compareTo(MyClass a, MyClass b){ return a.val - b.val //increasing (minHeap) //return b.val - a.val //decreasing (maxHeap) } } MyComparator myComparator = new MyComparator(); // 决定最大还是最小堆 PriorityQueue<MyClass> heap = new PriorityQueue<MyClass>(capacity, myComparator);- Comparable: adj, 如果一个类是comparable,表示它的实例知道如何去和其它实例进行比较
class MyClass implements Comparable<MyClass>{ @override public int compareTo(final MyClass a){ return this.val - o.val //increasing (minHeap) //return o.val - this.val //decreasing (maxHeap) } } PriorityQueue<> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(capacity); //最小堆
应用: 动态流动的 数据流 的情况
11. HashMap & HashSet
HashMap
在Java 里,Map是一个Interface,需要不同的类去实现,如HashMap 等
例如 Map<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap();
基本操作
- (boolean) put O(1)
- remove O(1)
- containsKey O(1)
- get O(1)
- containsValue O(n)
- entrySet, keySet, values
example:
hashMap: [<'apple', 1>,<'pear', 1>];
hashMap.put('banana', 3);
hashMap.remove('apple');
hashMap.get('pear');
hashMap.containKey('Kiwi')
hashMap.containValue(3)
遍历
for(Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.printIn('Key:' + entry.getKey() + '; Value: ' + entry.getValue());
}
Hash Function
用来快速通过key 去匹配value的地址
- open hashing
- close hashing
HashCode &Equals